Exploring the Cryptic Power of Sanskrit: Insights from Project SHIVOHAM
Sanskrit, often regarded as one of the most cryptic and profound languages, holds secrets that have been passed down through generations. This blog delves into the fascinating aspects of Sanskrit as explored in the documentary ‘SUTRA – The Cryptic Power of Sanskrit’, uncovering its educational significance and the unique methodologies that have shaped its study.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Sanskrit
- Historical Significance of Sanskrit
- Educational Systems in Ancient India
- Guru-Shishya Tradition
- Memorization Techniques in Sanskrit Education
- Importance of Vedas and Other Texts
- The Role of Rhythm in Learning
- Sanskrit’s Influence on Indian Culture
- The Concept of Sutras
- Sutras and Their Applications
- The Power of Language in Communication
- Sanskrit vs. Other Languages
- Sanskrit in Modern Context
- Future of Sanskrit Education
- Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of Sanskrit
- FAQs about Sanskrit and Its Educational Impact
Introduction to Sanskrit
Sanskrit, one of the oldest languages in the world, serves as a cornerstone of Indian culture and education. It is not merely a language; it embodies the philosophical and spiritual essence of ancient Indian civilization. Known for its intricate grammar and rich vocabulary, Sanskrit offers a unique framework for expressing complex ideas and concepts.
With roots tracing back thousands of years, Sanskrit has significantly influenced many modern languages in the Indian subcontinent. Its systematic structure allows for precise communication, making it a valuable tool for scholars, linguists, and philosophers alike.

Characteristics of Sanskrit
- Phonetics: Sanskrit is known for its phonetic richness, with a wide range of sounds that can convey nuanced meanings.
- Grammar: It has a highly sophisticated grammatical structure, which includes a system of roots, prefixes, and suffixes that allows for the creation of numerous words from a single root.
- Literary Tradition: Sanskrit boasts a vast literary corpus, ranging from religious texts like the Vedas to epic narratives such as the Mahabharata and Ramayana.
Historical Significance of Sanskrit
The historical significance of Sanskrit extends beyond its role as a language. It is a key to understanding the cultural, religious, and philosophical developments of ancient India. Scholars believe that Sanskrit was used in various fields, including mathematics, astronomy, and medicine.
Throughout history, Sanskrit has served as the medium for transmitting knowledge across generations. Its preservation in manuscripts and oral traditions demonstrates its enduring importance in Indian education and society.

Sanskrit in Ancient India
- Religious Texts: The Vedas, Upanishads, and Puranas are foundational texts written in Sanskrit, providing insights into the spiritual and philosophical thought of the time.
- Philosophy and Science: Philosophers like Adi Shankaracharya and mathematicians like Aryabhata contributed to various fields using Sanskrit, establishing its role in scientific discourse.
- Cultural Transmission: Sanskrit facilitated cultural exchange and the spread of ideas across Asia, influencing languages and cultures in regions such as Southeast Asia.

Educational Systems in Ancient India
Education in ancient India was highly structured and revered, with a strong emphasis on oral transmission of knowledge. The Gurukula system allowed students to learn directly from their teachers (gurus) in a residential setting, fostering a close mentor-student relationship.
Subjects included not only languages but also sciences, mathematics, philosophy, and arts, all delivered in Sanskrit. This comprehensive approach to education ensured that students had a well-rounded understanding of their culture and the world.

Curriculum and Learning Methods
- Vedic Studies: Students studied the Vedas, learning hymns and rituals that were integral to spiritual practices.
- Philosophy and Logic: Discourses on various philosophies were common, encouraging critical thinking and debate.
- Mathematics and Astronomy: Students were trained in mathematical concepts and astronomical observations, emphasizing the application of Sanskrit in scientific inquiry.
Guru-Shishya Tradition
The Guru-Shishya tradition is a hallmark of ancient Indian education, where the relationship between the teacher and student is central. This tradition emphasizes personal attention, mentorship, and the transfer of knowledge through direct interaction.
In this system, students often lived with their gurus, learning not only academic subjects but also ethics, values, and life skills. This holistic approach fostered deep respect for knowledge and learning.
Key Features of the Tradition
- Personalized Learning: The guru tailored teachings to the individual needs and abilities of the student.
- Respect and Discipline: Students were expected to show utmost respect to their gurus, which was integral to the learning process.
- Oral Transmission: Knowledge was primarily passed down orally, ensuring the preservation of texts and teachings.

Memorization Techniques in Sanskrit Education
Memorization played a crucial role in Sanskrit education, as many texts were transmitted orally before being written down. Techniques such as rhythmic recitation and mnemonic devices were employed to aid memory retention.
Students learned to memorize vast amounts of text, including scriptures and philosophical works, which not only enhanced their cognitive abilities but also instilled a deep understanding of the material.
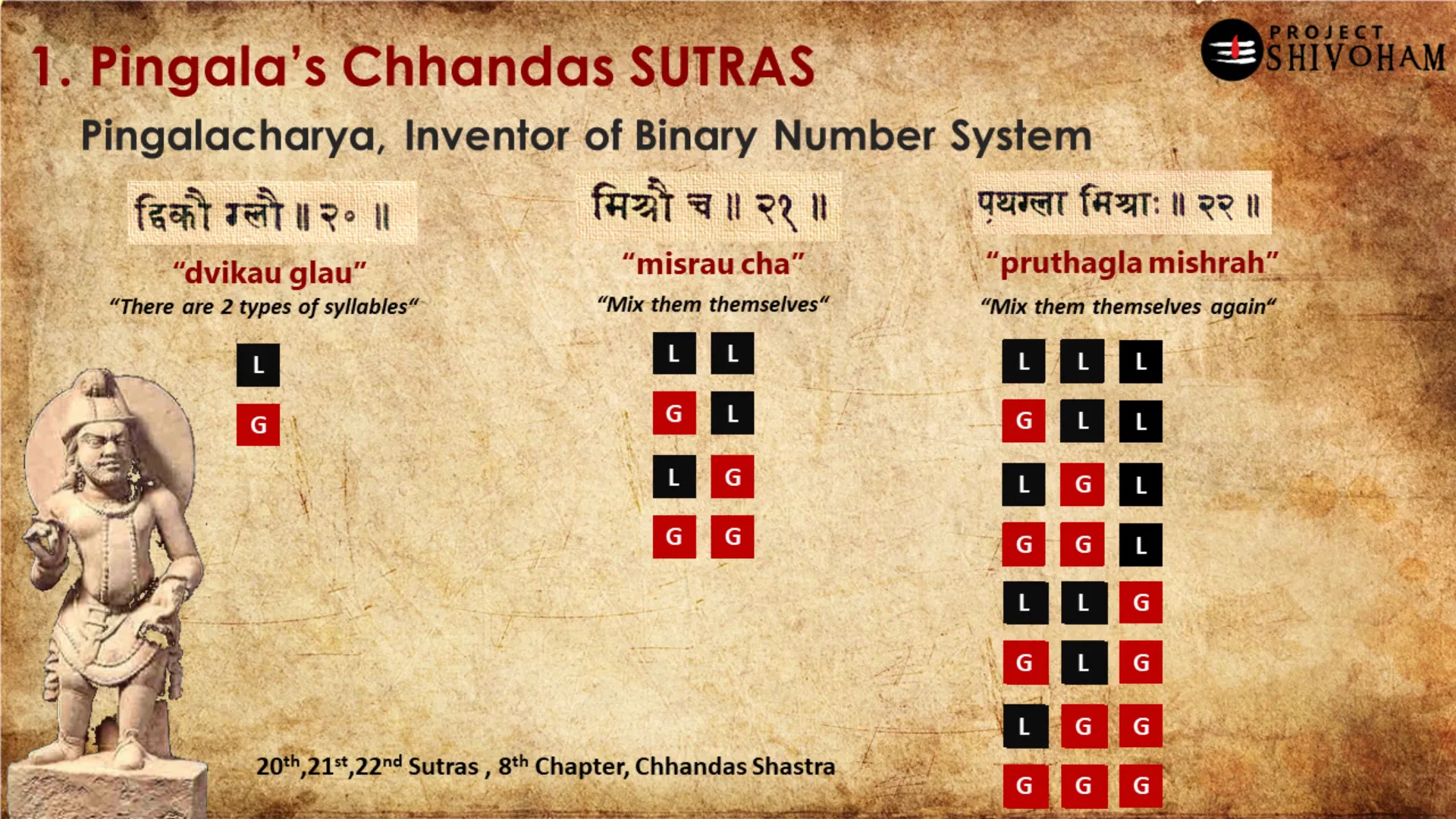
Effective Memorization Strategies
- Chanting: Reciting verses aloud helped reinforce memory through auditory learning.
- Repetition: Regular repetition of texts ensured familiarity and retention.
- Visualization: Associating concepts with visual imagery aided in recalling complex ideas.

Importance of Vedas and Other Texts
The Vedas are considered the oldest sacred texts in Sanskrit and are foundational to Hindu philosophy and rituals. Their significance extends beyond religion, influencing various fields such as ethics, politics, and art.
Other texts, including the Upanishads and Puranas, further elaborate on Vedic teachings, offering insights into metaphysics, cosmology, and the nature of existence. These works continue to be studied and revered, underscoring their timeless relevance.
Vedic Literature
- Rigveda: The oldest Veda, consisting of hymns dedicated to various deities.
- Samaveda: Known for its musical chants, it forms the basis of Indian classical music.
- Yajurveda: Contains prose mantras for rituals and sacrifices.
- Atharvaveda: Focuses on everyday life and practical knowledge.
The Role of Rhythm in Learning
Rhythm plays a pivotal role in the learning process, particularly in the context of Sanskrit education. The rhythmic patterns inherent in Sanskrit texts facilitate memorization and comprehension. This connection between rhythm and learning is not merely coincidental; it is a foundational aspect of how knowledge was traditionally imparted.
In Sanskrit, each verse is often set to a specific meter, creating a musical quality that enhances recall. This rhythmic recitation allows students to internalize complex concepts effortlessly, transforming learning into an engaging auditory experience.
Benefits of Rhythmic Learning
- Enhanced Memorization: The musicality of rhythmic patterns makes it easier for learners to memorize verses and texts.
- Increased Engagement: Rhythm captures attention, making the learning process more enjoyable and interactive.
- Cognitive Development: Engaging with rhythm stimulates different areas of the brain, fostering critical thinking and analytical skills.
Sanskrit’s Influence on Indian Culture
Sanskrit’s impact on Indian culture is profound and far-reaching. As the language of ancient texts, it has shaped religious, philosophical, and artistic expressions across centuries. The cultural significance of Sanskrit extends beyond literature; it is embedded in rituals, music, dance, and art forms that define Indian heritage.
From the recitation of Vedic hymns during religious ceremonies to the use of Sanskrit in classical music compositions, its influence permeates various aspects of life in India. This cultural resonance underscores the importance of preserving and promoting Sanskrit education today.

Key Cultural Contributions
- Religious Practices: Sanskrit is the language of the Vedas and other sacred texts, forming the basis of Hindu rituals and ceremonies.
- Literature and Arts: The epic narratives of the Mahabharata and Ramayana, along with classical poetry, showcase the literary richness of Sanskrit.
- Philosophy and Thought: The philosophical discourses found in the Upanishads have influenced spiritual thought and practice in India and beyond.

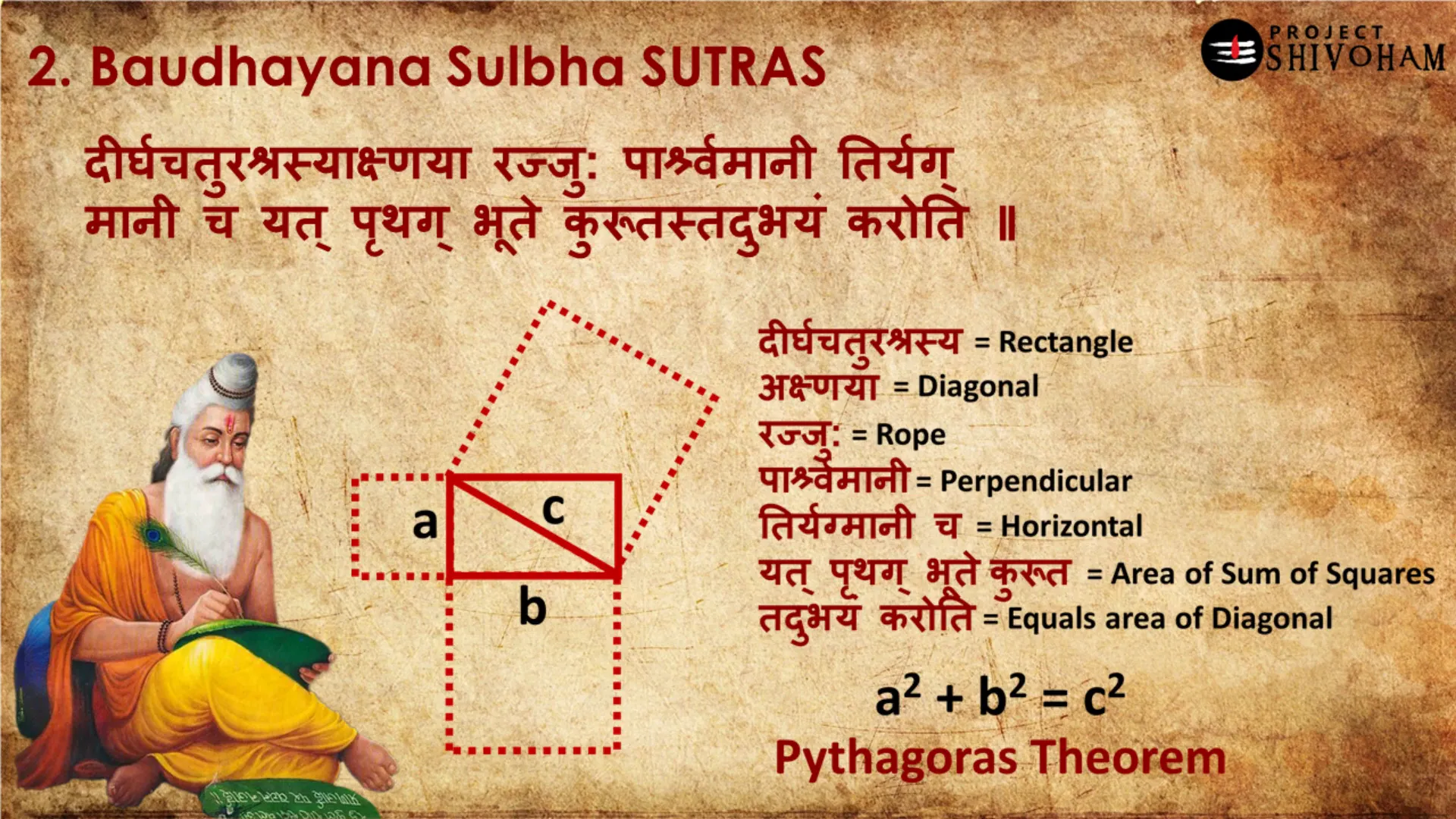
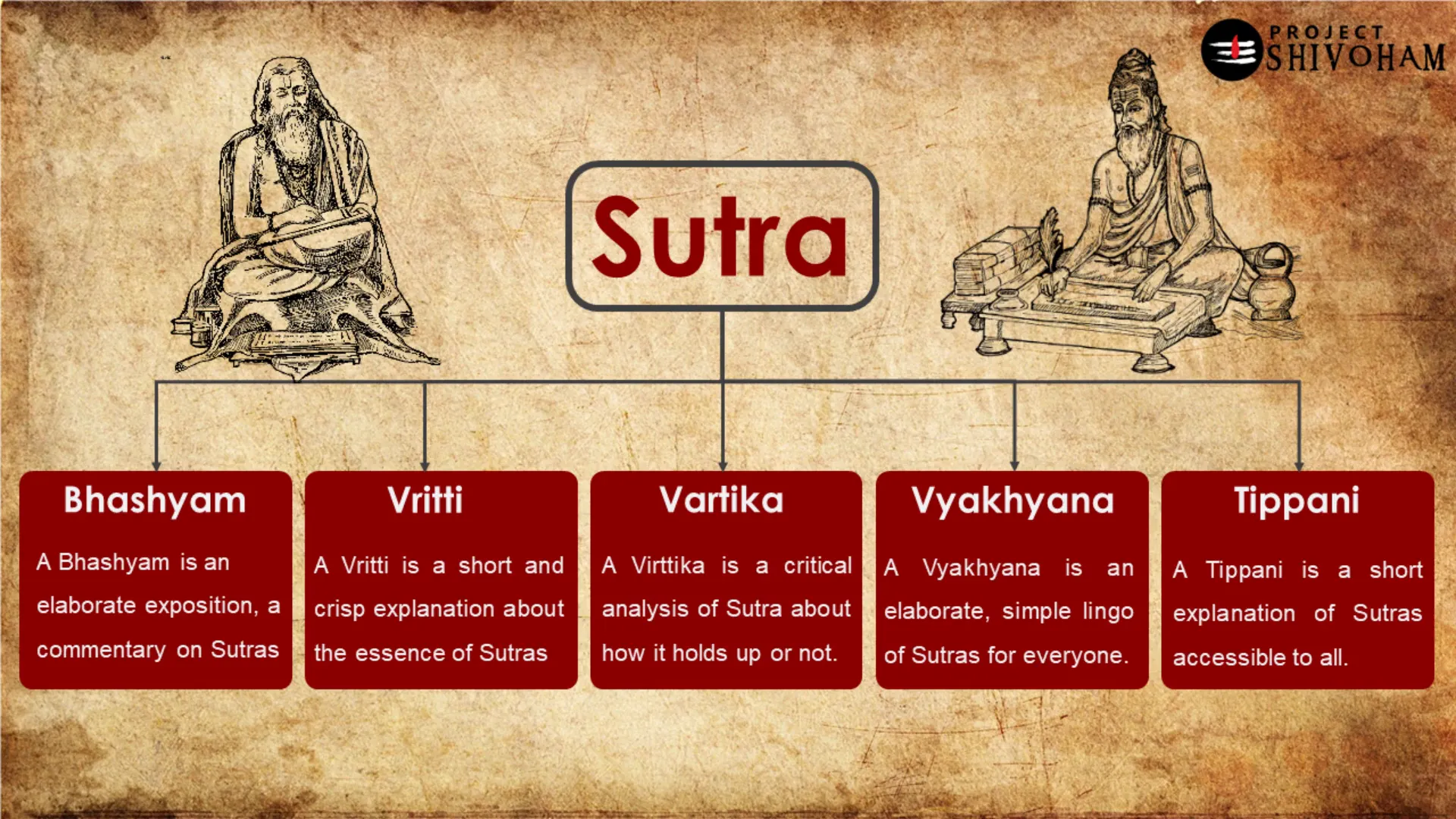
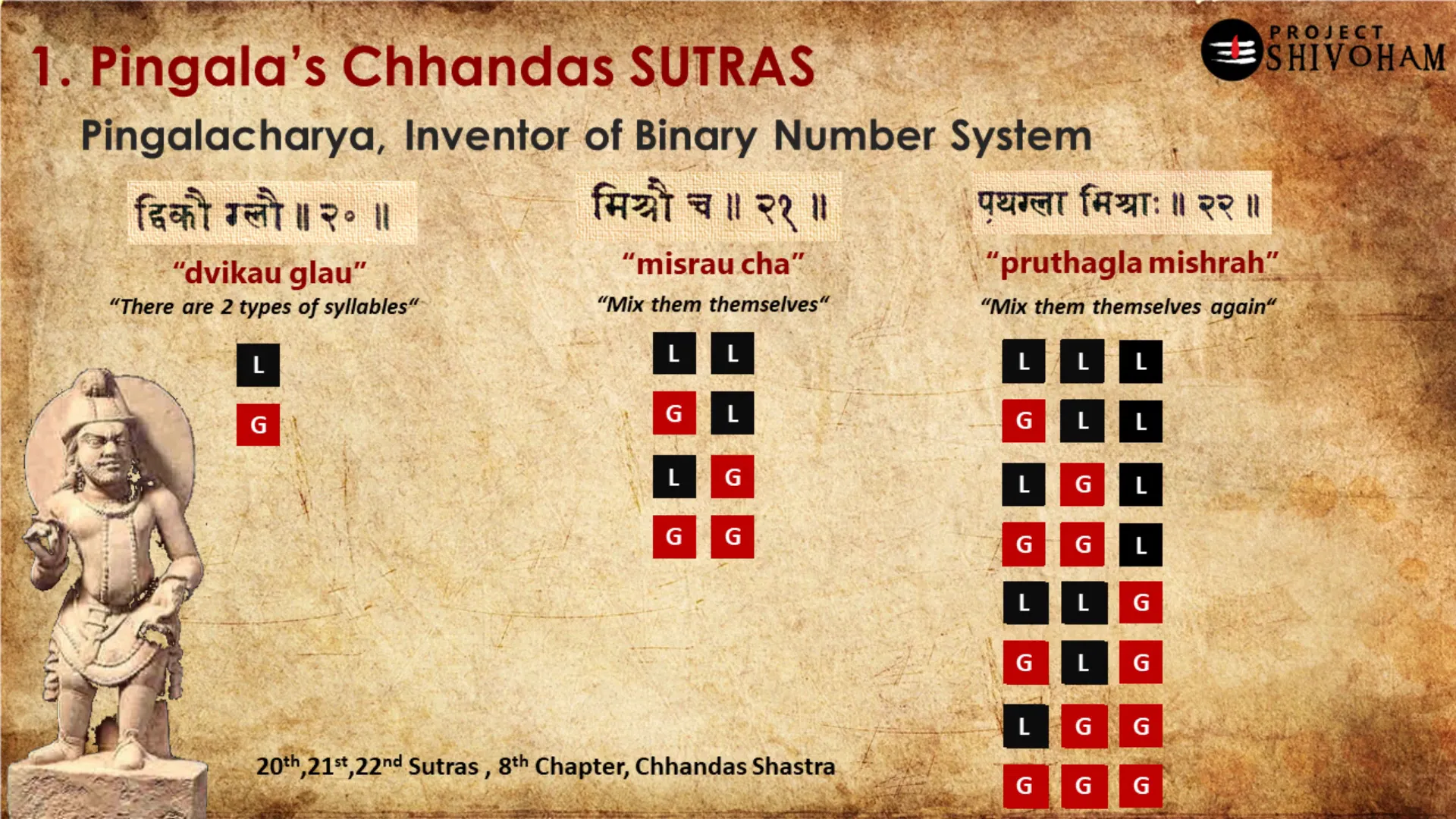
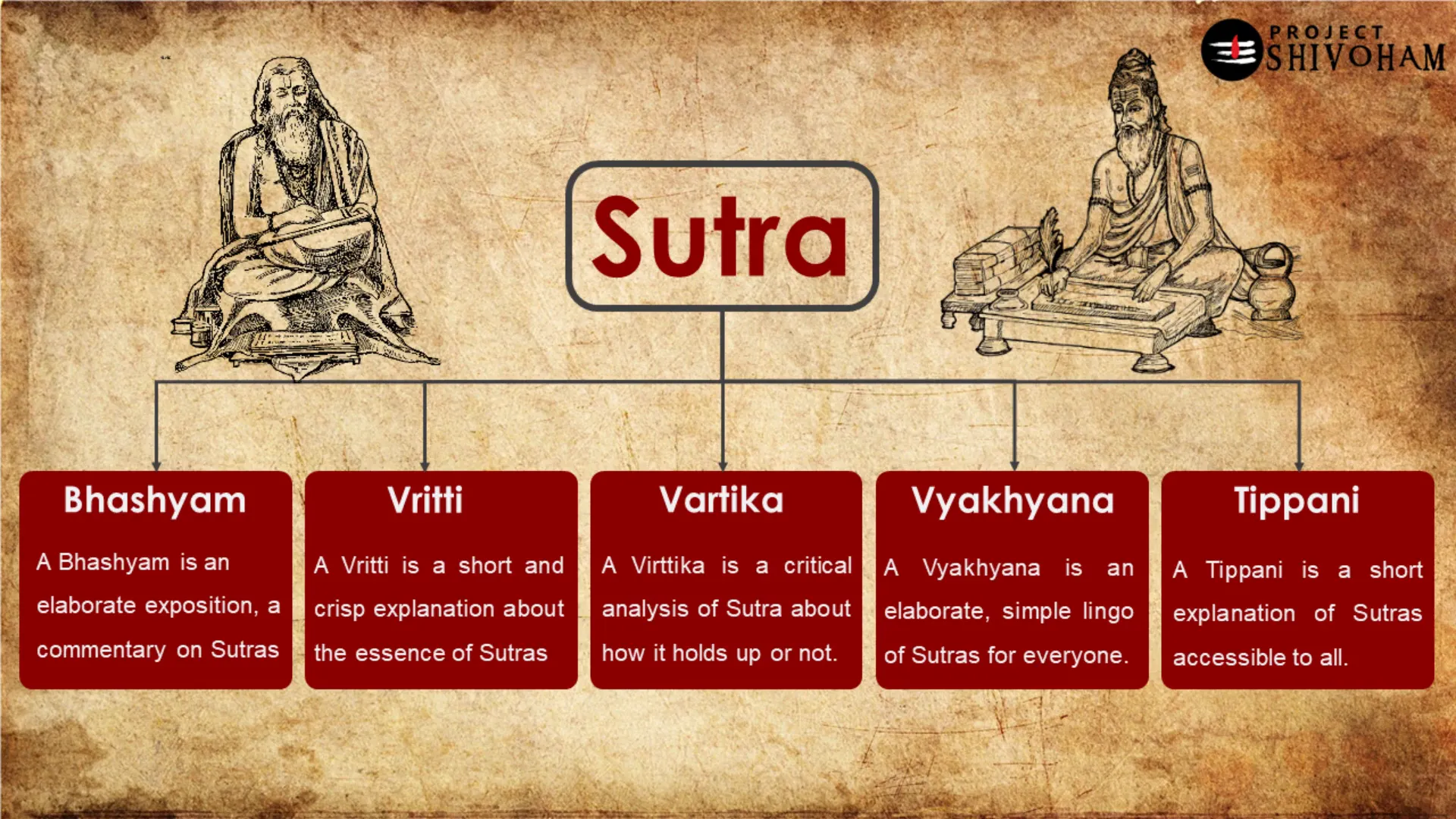
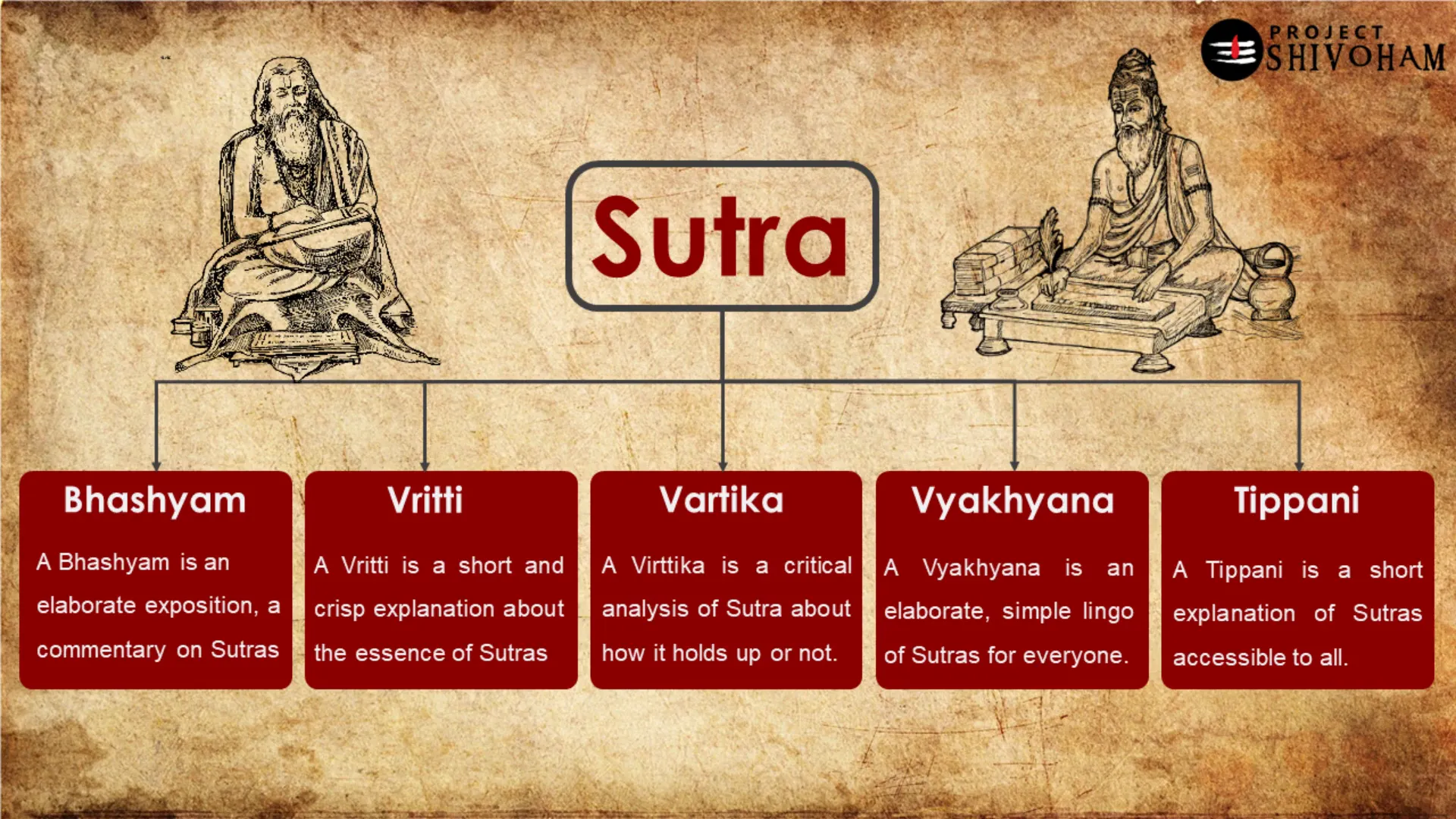
The Concept of Sutras
Sutras are concise aphorisms or statements that convey complex ideas in a compact form. In Sanskrit literature, they serve as foundational texts across various disciplines, including philosophy, grammar, and yoga. The structure of sutras allows for deep exploration of subjects while maintaining clarity and precision.
The term “sutra” itself means “thread,” symbolizing how these brief statements connect diverse concepts and teachings. This thread-like quality enables learners to weave together intricate ideas, fostering a comprehensive understanding of the subject matter.

Characteristics of Sutras
- Conciseness: Sutras are designed to be brief yet impactful, allowing for easy memorization and recall.
- Layered Meaning: Each sutra often holds multiple interpretations, inviting deeper contemplation and discussion.
- Interconnectedness: Sutras are interrelated, forming a cohesive framework for understanding complex philosophies.

Sutras and Their Applications
The application of sutras extends across various fields, including philosophy, linguistics, and yoga. Each domain utilizes sutras to encapsulate foundational principles, guiding practitioners and scholars alike. The versatility of sutras makes them invaluable tools for both learning and teaching.
In the realm of yoga, for instance, the Yoga Sutras of Patanjali provide essential guidelines for practitioners. These sutras outline the path to spiritual enlightenment and self-realization, emphasizing the importance of discipline and meditation.

Applications in Different Fields
- Philosophy: Sutras encapsulate philosophical doctrines, making complex ideas accessible to learners.
- Grammar: Panini’s Ashtadhyayi uses sutras to explain the intricacies of Sanskrit grammar systematically.
- Yoga: The Yoga Sutras provide a roadmap for spiritual practice, detailing the principles of yoga and meditation.
The Power of Language in Communication
Language is a powerful tool for communication, shaping how individuals express thoughts, emotions, and ideas. In the context of Sanskrit, the language’s structure and vocabulary allow for nuanced expression, making it particularly effective in conveying complex philosophical concepts.
Furthermore, Sanskrit’s precision and clarity foster deeper connections between speakers and listeners. The use of specific terms and phrases enhances understanding, allowing for meaningful dialogue and exchange of ideas.

Impact of Sanskrit on Communication
- Clarity of Thought: The systematic structure of Sanskrit promotes clear articulation of ideas.
- Emotional Resonance: The rich vocabulary enables speakers to express a wide range of emotions effectively.
- Cross-Cultural Dialogue: Sanskrit serves as a bridge for communication among diverse cultures, facilitating the exchange of knowledge.

Sanskrit vs. Other Languages
When compared to other languages, Sanskrit stands out for its unique characteristics and historical significance. Its systematic grammar and phonetics provide a level of precision that many modern languages lack. This makes Sanskrit a powerful tool for scholarly inquiry and philosophical exploration.
Additionally, the ability of Sanskrit to convey complex concepts in a compact form through sutras is unparalleled. This efficiency in communication highlights the language’s sophistication and relevance in contemporary discourse.

Comparative Analysis
- Grammatical Structure: Sanskrit’s grammatical rules are more systematic compared to many modern languages, allowing for greater flexibility in expression.
- Phonetic Richness: The phonetic diversity of Sanskrit enables the articulation of subtle distinctions in meaning.
- Cultural Legacy: Unlike many languages, Sanskrit carries an extensive cultural and philosophical heritage that continues to influence modern thought.

Sanskrit in Modern Context
In contemporary society, Sanskrit is often perceived as an ancient language, yet its relevance persists in various domains. From academic institutions to spiritual practices, Sanskrit continues to play a vital role. Its structured grammar and rich vocabulary allow for profound expression, making it an invaluable asset in modern education and cultural practices.
Many universities across the globe have integrated Sanskrit studies into their curricula, recognizing its significance in understanding ancient texts and philosophies. Moreover, the revival of interest in yoga and meditation has further propelled the usage of Sanskrit, particularly in the context of spiritual and wellness practices.
Applications of Sanskrit Today
- Academic Research: Scholars utilize Sanskrit to study ancient literature, philosophy, and sciences, contributing to interdisciplinary research.
- Spiritual Practices: Many modern spiritual movements and yoga practices incorporate Sanskrit chants and texts, enhancing the depth of the experience.
- Technology and Linguistics: Sanskrit’s precise structure has inspired advancements in computational linguistics and artificial intelligence, particularly in natural language processing.
Future of Sanskrit Education
The future of Sanskrit education appears promising, with increasing interest among students and educators. Initiatives aimed at revitalizing Sanskrit through modern pedagogical methods are gaining traction. This includes the use of technology in teaching, such as online courses and digital resources that make learning more accessible.
Additionally, there is a growing recognition of the importance of preserving ancient knowledge systems. Educational institutions are beginning to adopt innovative teaching techniques that emphasize experiential learning and cultural immersion, making Sanskrit more relatable to younger generations.

Innovative Teaching Methods
- Digital Learning Platforms: Online platforms provide resources and courses for learners worldwide, promoting a global interest in Sanskrit.
- Interactive Workshops: Hands-on workshops and cultural events engage students in practical applications of Sanskrit, enhancing their learning experience.
- Integration with Other Disciplines: Combining Sanskrit with subjects like philosophy, linguistics, and history creates a holistic educational approach.
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of Sanskrit
The legacy of Sanskrit is profound, transcending time and cultural boundaries. As we navigate the complexities of the modern world, the teachings and philosophies embedded in Sanskrit provide valuable insights into human existence. Its emphasis on clarity of thought, ethical living, and intellectual inquiry remains relevant today.
By fostering a renewed interest in Sanskrit, we not only preserve an ancient language but also enrich our understanding of diverse cultural heritages. The continued study and application of Sanskrit will ensure its survival and relevance for future generations.
FAQs about Sanskrit and Its Educational Impact
What is the importance of learning Sanskrit in today’s world?
Learning Sanskrit offers insights into ancient philosophies and texts that have shaped many modern disciplines. It enhances cognitive skills and provides a deeper understanding of various cultural and spiritual practices.
How does Sanskrit influence other languages?
Sanskrit has significantly influenced many languages, particularly in South Asia. Its grammatical structures and vocabulary can be seen in languages like Hindi, Bengali, and many others, showcasing its lasting impact on linguistic development.
Can Sanskrit be useful in modern technology?
Yes, the structured nature of Sanskrit has made it a subject of interest in fields like artificial intelligence and computational linguistics. Its precise grammar aids in the development of algorithms for natural language processing.
What are the challenges in teaching Sanskrit today?
Challenges include a lack of qualified teachers, limited resources, and misconceptions about the relevance of Sanskrit in modern education. Addressing these issues requires innovative approaches and increased awareness of its benefits.
Courtesy: Aravind Markandeya, Project Shivoham