Exploring the Roots of Indian Languages: The Significance of Shiva Sutras
The rich tapestry of Indian languages traces back to the ancient Shiva Sutras, a foundational text influencing linguistics and phonetics. This blog delves into the historical, cultural, and linguistic significance of these sutras, shedding light on India’s diverse language heritage.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to India’s Linguistic Diversity
- The Connection Between Language and Culture
- The Importance of Preserving Language Heritage
- Impacts of Modernization on Language
- Conclusion: Embracing Linguistic Diversity
- Frequently Asked Questions
Introduction to India’s Linguistic Diversity
India stands as a vibrant mosaic of languages, with over 1,600 distinct languages spoken across its vast landscape. This diversity is not merely a matter of communication but a reflection of the country’s rich cultural heritage. Each language carries its own historical significance, traditions, and nuances, contributing to the collective identity of the Indian populace.
The linguistic diversity in India can be attributed to various factors, including its geographical expanse, historical migrations, and cultural exchanges. From the Indo-Aryan languages predominantly spoken in the northern regions to the Dravidian languages in the south, the spectrum of languages showcases the evolution of human interaction and social structures over millennia.

Historical Context of Indian Languages
The history of Indian languages dates back thousands of years, intertwining with the evolution of civilization in the region. The earliest evidence of language use can be traced to the Indus Valley Civilization, where inscriptions suggest a rich linguistic culture. However, it is with the arrival of the Indo-Aryan languages, around 1500 BCE, that the linguistic landscape began to transform significantly.
As various dynasties rose and fell, languages evolved, borrowed, and blended, leading to the emergence of regional dialects. Sanskrit, as a classical language, played a pivotal role in shaping many modern languages in India, providing a foundation for grammar, vocabulary, and literary traditions.

The Role of Shiva Sutras in Linguistics
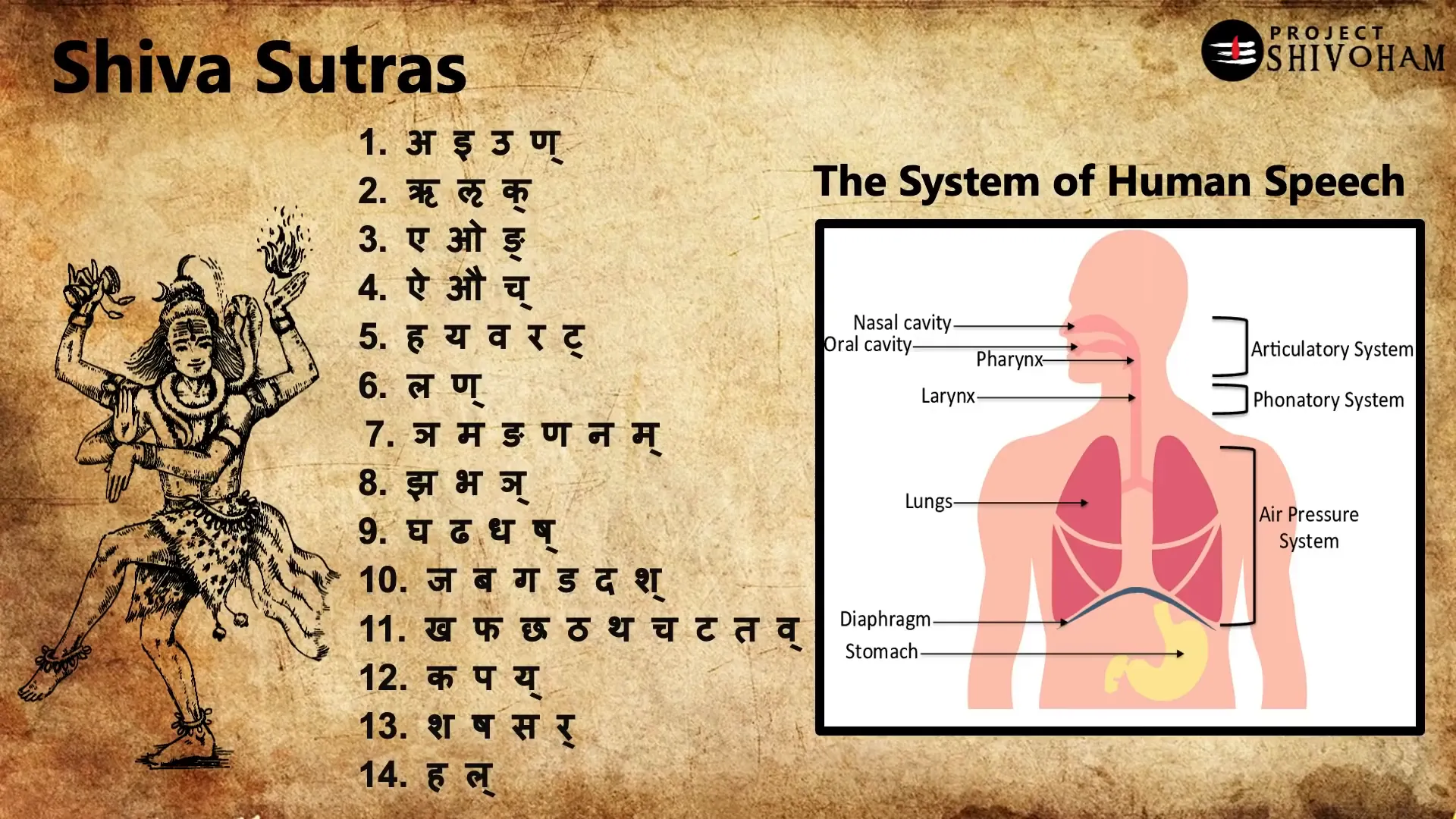
The Shiva Sutras are considered a cornerstone in the study of linguistics, particularly in understanding the structure of language and its philosophical implications. These ancient texts provide insights into the relationship between sound and meaning, emphasizing the significance of phonetics in language formation.
Through the lens of the Shiva Sutras, language is perceived not just as a tool for communication but as a medium that connects the individual to the cosmic order. This philosophical approach laid the groundwork for subsequent linguistic theories and practices in India.
Pāṇini and the Ashtadhyayi
Pāṇini, an eminent ancient grammarian, is renowned for his seminal work, the Ashtadhyayi. This text is regarded as one of the most comprehensive grammatical treatises in the history of linguistics. Pāṇini’s methodology involved analyzing the structure of Sanskrit through a series of rules and principles, establishing a systematic approach to grammar.
The Ashtadhyayi consists of around 4,000 sutras, which outline the formation of words and sentences. Pāṇini’s work not only codified the grammatical rules of Sanskrit but also influenced the study of linguistics globally, inspiring scholars across cultures to explore the intricacies of language.

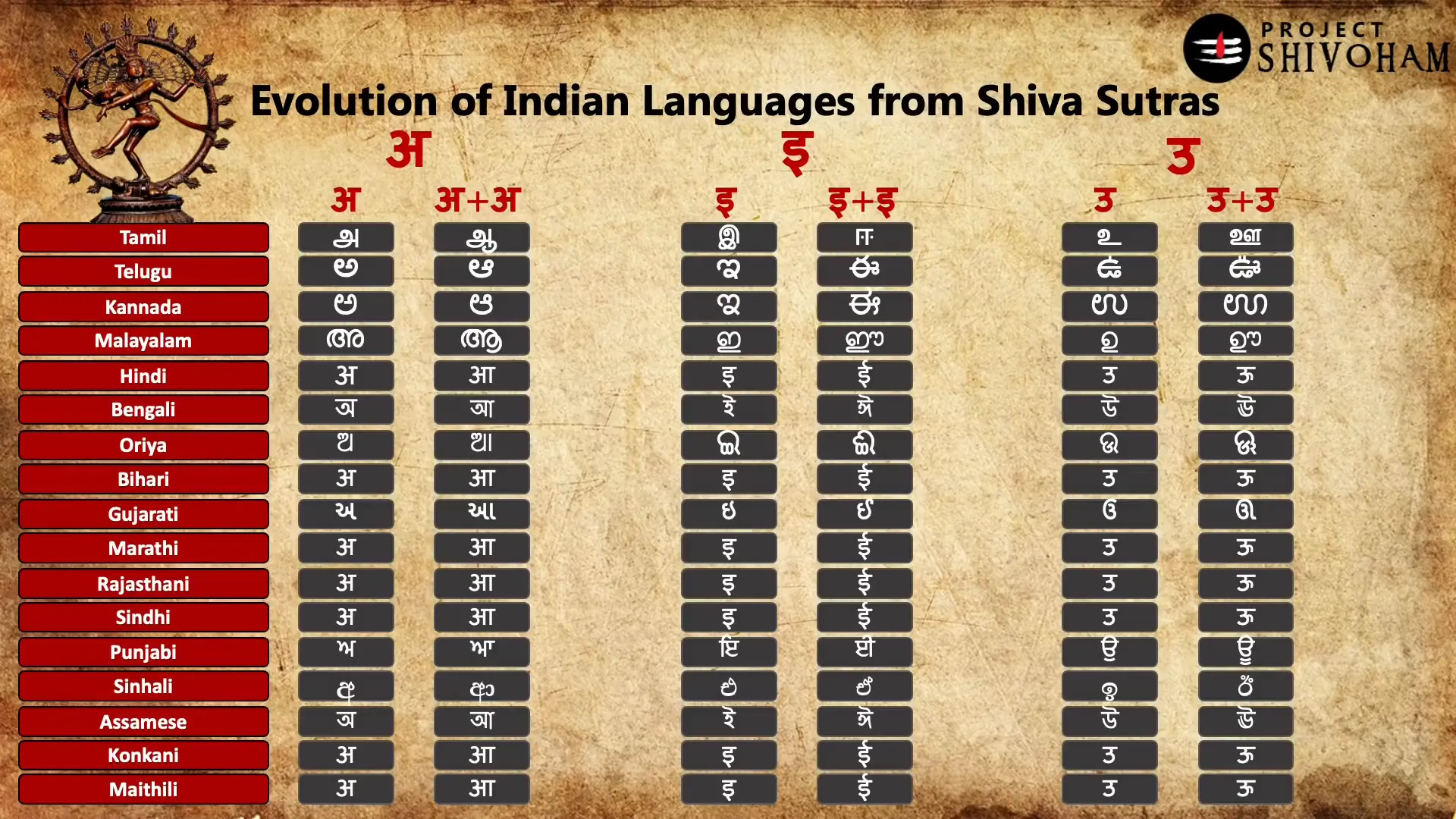
Understanding the Mother of All Languages
Many linguists and scholars refer to Sanskrit as the ‘Mother of All Languages’ due to its profound influence on numerous languages spoken today in India and beyond. Its grammatical precision and rich vocabulary have made it a reference point for language development in the Indo-European family.
The linguistic structures found in Sanskrit have permeated various regional languages, contributing to their evolution and diversity. This interconnectedness reinforces the idea that languages are not isolated entities but rather a continuum shaped by historical, cultural, and social dynamics.

The Evolution of Language in India
The evolution of languages in India is a testament to the dynamic interplay of culture, society, and historical events. From ancient scriptures to modern-day dialects, the linguistic landscape continues to evolve, reflecting the changes in society and technology.
With globalization and the rise of digital communication, languages are experiencing both challenges and transformations. The preservation of linguistic diversity is crucial, as it not only embodies cultural heritage but also fosters a sense of identity among communities.
The Connection Between Language and Culture
Language serves as a powerful vehicle for cultural expression and identity. It encapsulates the beliefs, traditions, and values of a community, reflecting its unique worldview. In India, each language tells a story, revealing the intricate relationship between linguistic diversity and cultural heritage.
The nuances in language often mirror the nuances in culture. For instance, certain words or phrases may exist in one language but have no direct translation in another, highlighting specific cultural practices or beliefs. This connection fosters a deeper understanding of the societal norms and values that shape the lives of people within a particular linguistic group.

Language as a Cultural Identifier
Language is not merely a communication tool; it is a marker of identity. In many Indian communities, speaking a particular language can signify belonging to a specific cultural group. This identity is often reinforced through rituals, folklore, and traditional practices that are passed down through generations.
Moreover, language plays a vital role in the preservation of history and cultural narratives. Oral traditions, often the backbone of many Indian cultures, rely heavily on language to convey stories, wisdom, and lessons from the past. Thus, the loss of a language can lead to the erosion of cultural heritage.
The Importance of Preserving Language Heritage
Preserving language heritage is crucial for maintaining cultural diversity and fostering a sense of identity. As languages face extinction due to globalization and modernization, the need for preservation becomes increasingly urgent.
Efforts to document and revitalize endangered languages can help communities reconnect with their roots. This can involve creating educational programs, promoting literature in native languages, and encouraging intergenerational transmission of language skills.
Benefits of Language Preservation
- Cultural Continuity: Preserving languages ensures that cultural practices and traditions are passed down to future generations.
- Identity and Belonging: A shared language fosters a sense of community and belonging among speakers.
- Diversity in Thought: Different languages offer unique perspectives and ways of thinking, enriching global discourse.
In India, initiatives aimed at revitalizing regional languages can significantly impact local communities, providing them with a stronger sense of identity and cultural pride.

Impacts of Modernization on Language
Modernization has brought significant changes to the way languages are spoken and perceived. The rise of technology and digital communication has influenced language use, often leading to the simplification of language structures.
While modernization can facilitate communication across diverse linguistic backgrounds, it can also lead to the homogenization of languages. The dominance of global languages, particularly English, poses a threat to regional languages, which may see a decline in usage among younger generations.
Challenges Faced by Regional Languages
- Declining Usage: As younger generations gravitate towards dominant languages for educational and professional opportunities, regional languages are at risk of becoming obsolete.
- Loss of Linguistic Nuance: The simplification of language in digital communication can strip away the richness and depth of regional dialects.
- Limited Resources: Many regional languages lack sufficient educational materials and platforms for learning, making it difficult for speakers to maintain fluency.
Addressing these challenges requires collaborative efforts among communities, governments, and educational institutions to promote and support linguistic diversity.
Conclusion: Embracing Linguistic Diversity
Embracing linguistic diversity is essential for fostering a rich cultural tapestry in society. Each language holds a unique perspective, contributing to the global dialogue on identity, tradition, and community.
By valuing and promoting linguistic diversity, we not only preserve cultural heritage but also enrich our collective human experience. It is imperative to support initiatives that encourage language learning and cultural exchange, ensuring that the voices of all communities are heard and celebrated.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of preserving endangered languages?
Preserving endangered languages is crucial for maintaining cultural diversity, fostering identity, and ensuring the transmission of traditional knowledge and practices to future generations.
How can individuals contribute to language preservation?
Individuals can contribute by learning their native languages, participating in community language programs, and advocating for the inclusion of regional languages in educational curricula.
What role does technology play in language evolution?
Technology can facilitate communication and access to information, but it can also lead to the simplification and potential decline of regional languages due to the dominance of global languages.
Courtesy: Aravind Markandeya @project shivoham
